Skin, the body’s largest organ, is our first line of defense against the outside world. It’s a complex system that not only protects us but also communicates our health and well-being. However, it’s not immune to disorders. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of common skin disorders, their causes, symptoms, and treatments.
Skin disorders are as diverse as they are prevalent. From temporary conditions like acne to more persistent ones like psoriasis, these disorders can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe physical and emotional distress. But fear not! Understanding these conditions is the first step towards effective treatment.
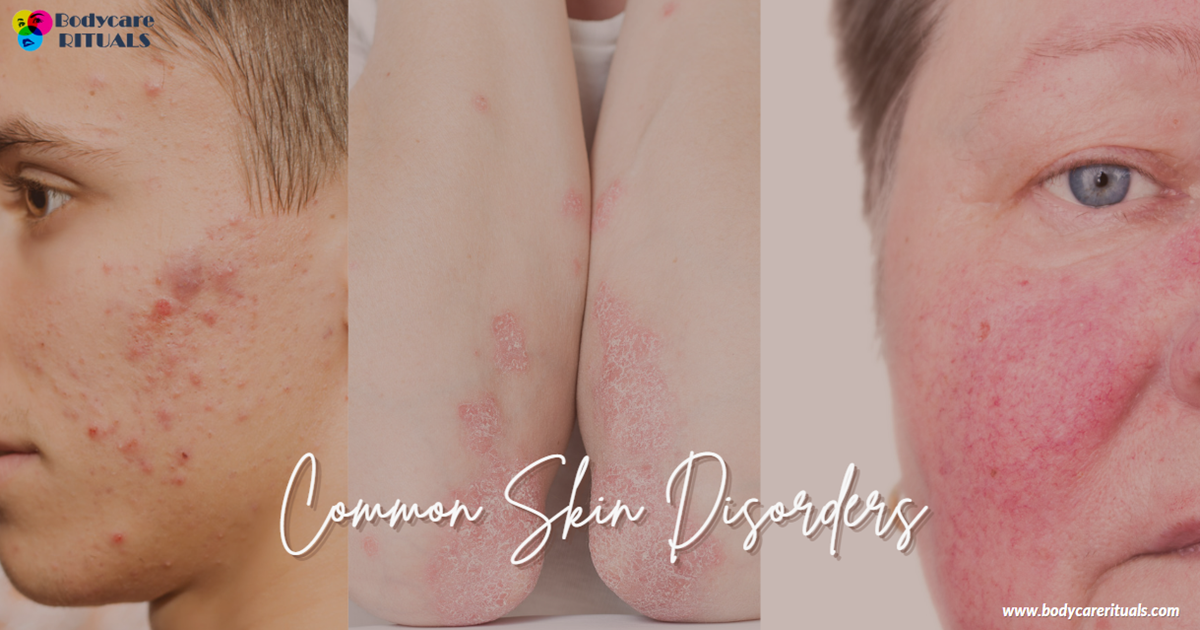
What are the most Common Skin Disorders?
Acne: More Than Just a Teenage Problem
Acne is one of the most common skin disorders, affecting people of all ages. It occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to whiteheads, blackheads, and pimples. While acne is often associated with adolescence, it can persist into adulthood and cause significant distress.
Treating Acne
Acne treatment is tailored to the severity of the condition and the individual’s skin type. For mild acne, over-the-counter products containing salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide can be effective. These ingredients work by reducing inflammation and treating mild bacterial infections.
For more severe cases, a dermatologist may prescribe topical retinoids or oral medications. Retinoids, such as tretinoin, adapalene, and isotretinoin, work by preventing the clogging of hair follicles. They can be prescribed as topical or oral medication and should be taken under physician supervision only.
- Antibiotics such as azithromycin, tetracycline, and amoxicillin can also be used to prevent the spread of bacterial infections. These are prescribed as topical and oral medications.
In addition to these, other treatments include keratolytic agents like salicylic acid that promote skin exfoliation, dicarboxylic acids like azelaic acid that reduce bacterial infection and inflammation, and sulfones like dapsone that reduce inflammation. In some cases, oral contraceptives and antiandrogens are also used to help control hormonal acne in women.
Cold Sores: A Common Viral Infection
Cold sores, also known as fever blisters, are a common viral infection. They present as painful, fluid-filled blisters around the mouth and lips. These sores can be accompanied by mild, flu-like symptoms such as a low fever, body aches, and swollen lymph nodes.
Treating Cold Sores
While there’s no cure for the virus that causes cold sores, antiviral medications can speed up healing and reduce the frequency of outbreaks. These medications include acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir. They can be prescribed as oral pills or creams to be applied on the sores. In severe cases, drugs are given in injection form.
- Pain can be managed with analgesics like ibuprofen and acetaminophen. It’s also important to maintain good hygiene and nutrition to hinder recurrence.
Psoriasis: A Persistent Skin Disorder
Psoriasis is a chronic skin disorder characterized by red, scaly patches of skin. It’s caused by an overactive immune system that speeds up the lifecycle of skin cells.
Treating Psoriasis
Treatment for psoriasis aims to slow skin cell turnover and reduce inflammation. This can involve topical treatments, light therapy, and systemic medications.
- Topical treatments include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogues, and retinoids. Corticosteroids are the most frequently prescribed medications for treating mild to moderate psoriasis. They are available in various forms, like oils, ointments, creams, lotions, gels, foams, sprays, and shampoos.
- Vitamin D analogues like calcipotriene and calcitriol work by slowing skin cell growth. Retinoids like tazarotene reduce inflammation.
- Light therapy involves exposure to UV rays, which slow down the formation of too many skin cells and help reduce scaling.
- Systemic medications include methotrexate, biologics like etanercept, ustekinumab, secukinumab, and immunosuppressants.
Rosacea: More Than Just a Blush
Rosacea is a chronic skin disease that causes persistent redness, visible blood vessels, and small, red, pus-filled bumps on the face. It can flare up for weeks or months and then diminish for a while.
Treating Rosacea
While there’s no cure for rosacea, treatments can control and reduce the signs and symptoms. These may include topical drugs to reduce redness and oral antibiotics to address inflammation.
- Topical treatments include dicarboxylic acids like azelaic acid that reduce facial redness. Oral antibiotics like doxycycline are used to fight infections, if any, and reduce inflammation.
- In severe cases, laser therapy is used to reduce redness from enlarged blood vessels. Dermabrasion, a procedure to remove skin, is also used.
Prevention is better than Cure
Understanding common skin disorders is crucial to managing them effectively. Remember, each skin disorder is unique and requires a tailored approach to treatment. It’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and treatment. In the end, our skin is a reflection of our overall health. By taking care of our skin, we’re taking care of our entire body. So, let’s give our skin the care it deserves.


